This document is a guide to the AppleScript language—its lexical conventions, syntax, keywords, and other elements. It is intended primarily for use with AppleScript 2.0 or later and macOS version 10.5 or later.
AppleScript 2.0 can use scripts developed for any version of AppleScript from 1.1 through 1.10.7, any scripting addition created for AppleScript 1.5 or later for macOS, and any scriptable application for Mac OS v7.1 or later. A script created with AppleScript 2.0 can be used by any version of AppleScript back to version 1.1, provided it does not use features of AppleScript, scripting additions, or scriptable applications that are unavailable in that version.
Important: Descriptions and examples for the terms in this document have been tested with AppleScript 2.0 in OS X v10.5 (Leopard). Except for terms that are noted as being new in Leopard, most descriptions and examples work with previous system versions, but have not been tested against all of them.
If you need detailed information about prior system and AppleScript versions, see AppleScript Release Notes (OS X v10.4 and earlier).
The program's installer files are commonly found as Editor.exe, script editor 2.exe, SCRiptEditor2.0.exe or SED.exe etc. May 19, 2011 - AppleScript Editor download for mac os x - The Script Editor is the application used to read, write, record, and save. Free Script Editor for Mac - Free downloads and reviews. 2) Run the AppleScript called “spreadsheetToJavaScript.app”. (To run it, either double-click the icon or open it in AppleScript Editor and run it from there. The AppleScript has finished when the contents of scripts/addAll.js have changed to match the changes that you made in the spreadsheet.) 3) Display the web page called “index.html”. If you are an experienced professional, chances are you have a good set of tools and a work process that you repeat on a daily basis to handle your work. That's good; it's how you become more productive, and become an expert. But with repetitive processes come repetitive mechanical work. Whether it's opening a file in Photoshop to change the format or adding an iCal to-do item based on an.
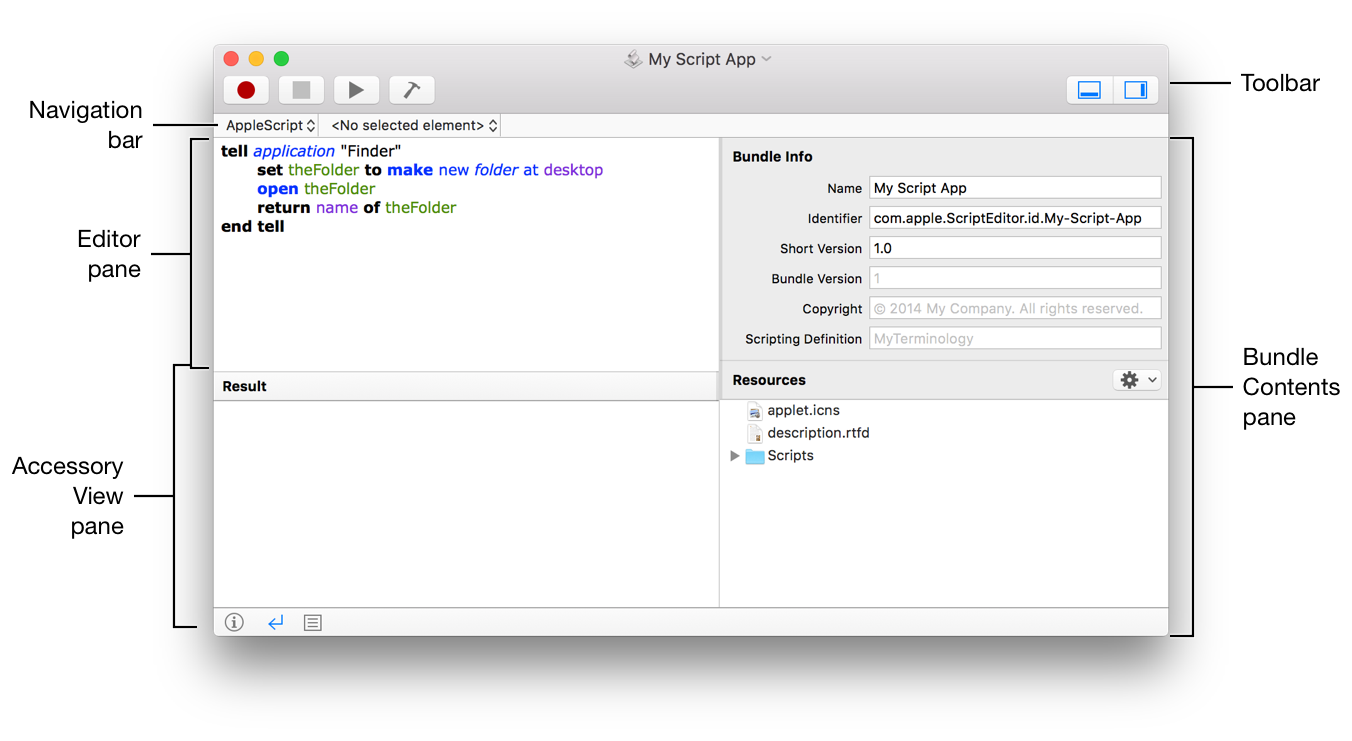
You can find this application in the AppleScript folder located in the Applications folder on your computer’s main hard drive. Navigate to this folder now and double-click the Script Editor icon to launch the application. NOTE: The following description and illustrations are for the Script Editor application included in Mac OSX 10.5. Board statistics Total number of registered users: 32,081 Total number of topics: 39,952 Total number of posts: 187,567 User information Newest registered user: Sonyminer Registered users online: 0 Guests online: 100.
What Is AppleScript?
AppleScript is a scripting language created by Apple. It allows users to directly control scriptable Macintosh applications, as well as parts of macOS itself. You can create scripts—sets of written instructions—to automate repetitive tasks, combine features from multiple scriptable applications, and create complex workflows.
Note: Apple also provides the Automator application, which allows users to automate common tasks by hooking together ready-made actions in a graphical environment. For more information, see Automator Documentation.
A scriptable application is one that can be controlled by a script. For AppleScript, that means being responsive to interapplication messages, called Apple events, sent when a script command targets the application. (Apple events can also be sent directly from other applications and macOS.)
AppleScript itself provides a very small number of commands, but it provides a framework into which you can plug many task-specific commands—those provided by scriptable applications and scriptable parts of macOS.
Most script samples and script fragments in this guide use scriptable features of the Finder application, scriptable parts of macOS, or scriptable applications distributed with macOS, such as TextEdit (located in /Applications).
Who Should Read This Document?
You should use this document if you write or modify AppleScript scripts, or if you create scriptable applications and need to know how scripts should work.
AppleScript Language Guide assumes you are familiar with the high-level information about AppleScript found in AppleScript Overview.
Organization of This Document
This guide describes the AppleScript language in a series of chapters and appendixes.
The first five chapters introduce components of the language and basic concepts for using it, then provide additional overview on working with script objects and handler routines:
AppleScript Lexical Conventions describes the characters, symbols, keywords, and other language elements that make up statements in an AppleScript script.
AppleScript Fundamentals describes basic concepts that underly the terminology and rules covered in the rest of this guide.
Variables and Properties describes common issues in working with variables and properties, including how to declare them and how AppleScript interprets their scope.
Script Objects describes how to define, initialize, send commands to, and use inheritance with script objects.
About Handlers provides information on using handlers (a type of function available in AppleScript) to factor and reuse code.
The following chapters provide reference for the AppleScript Language:
Class Reference describes the classes AppleScript defines for common objects used in scripts.
Commands Reference describes the commands that are available to any script.
Reference Forms describes the syntax for specifying an object or group of objects in an application or other container.
Operators Reference provides a list of the operators AppleScript supports and the rules for using them, along with sections that provide additional detail for commonly used operators.
Control Statements Reference describes statements that control when and how other statements are executed. It covers standard conditional statements, as well as statements used in error handling and other operations.
Handler Reference shows the syntax for defining and calling handlers and describes other statements you use with handlers.
The following chapter describes an AppleScript-related feature of macOS:
Folder Actions Reference describes how you can write and attach script handlers to specific folders, such that the handlers are invoked when the folders are modified.
The following appendixes provide additional information about the AppleScript language and how to work with errors in scripts:
AppleScript Keywords lists the keywords of the AppleScript language, provides a brief description for each, and points to related information.
Error Numbers and Error Messages describes error numbers and error messages you may see in working with AppleScript scripts.
Working with Errors provides detailed examples of handling errors with try Statements and error Statements.
Double Angle Brackets describes when you are likely to see double angle brackets (or chevrons—
«») in scripts and how you can work with them.Libraries using Load Script describes how to save libraries of handlers and access them from other scripts.
Unsupported Terms lists terms that are no longer supported in AppleScript.
Conventions Used in This Guide

Glossary terms are shown in boldface where they are defined.
Important: This document sometimes uses the continuation character (¬) for sample statements that don’t fit on one line on a document page. It also uses the continuation character in some syntax statements to identify an item that, if included, must appear on the same line as the previous item. The continuation character itself is not a required part of the syntax—it is merely a mechanism for including multiple lines in one statement.
The following conventions are used in syntax descriptions:
| Plain computer font indicates an element that you type exactly as shown. If there are special symbols (for example, |
placeholder | Italic text indicates a placeholder that you replace with an appropriate value. |
[optional] | Brackets indicate that the enclosed language element or elements are optional. |
(a group) | Parentheses group elements together. However, the parentheses shown in Handler Syntax (Positional Parameters) are part of the syntax. |
[optional]... | Three ellipsis points (...) after a group defined by brackets indicate that you can repeat the group of elements within brackets 0 or more times. |
a | b | c | Vertical bars separate elements in a group from which you must choose a single element. The elements are often grouped within parentheses or brackets. |
Filenames shown in scripts | Most filenames shown in examples in this document include extensions, such as To work with the examples on your computer, you may need to modify either that setting or the filenames. |
See Also
These Apple documents provide additional information for working with AppleScript:
See Getting Started with AppleScript for a guided quick start, useful to both scripters and developers.
See AppleScript Overview, including the chapter Scripting with AppleScript, for a high-level overview of AppleScript and its related technologies.
See Getting Started With Scripting & Automation for information on the universe of scripting technologies available in macOS.
See AppleScript Terminology and Apple Event Codes for a list of many of the scripting terms defined by Apple.
For additional information on working with the AppleScript language and creating scripts, see one of the comprehensive third-party documents available in bookstores and online.
Copyright © 2016 Apple Inc. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Updated: 2016-01-25
| Developer(s) | Apple Inc. |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 2.11 / August 18, 2018; 2 years ago[citation needed] |
| Operating system | Classic Mac OS, macOS |
| Type | Source code editor |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | developer.apple.com/library/archive/documentation/LanguagesUtilities/Conceptual/MacAutomationScriptingGuide/GettoKnowScriptEditor.html |
Script Editor (called AppleScript Editor from 2009 to 2014) is a code editor for the AppleScript and Javascript for Automation scripting languages, included in classic Mac OS and macOS.[1]
AppleScript Editor provides basic debugging capabilities[2] and can save AppleScripts as plain text (.applescript), as a compiled script (.scpt), as a script bundle (.scptd), or as an application (.app).[3][4] AppleScript Editor also handles script dictionary files, allowing the user to see what scripting classes and commands are available for each scriptable application installed on the computer.[5]
Prior to Mac OS X 10.3, Script Editor was developed using Carbon. 10.3 introduced a new Script Editor written using Cocoa. From Mac OS X 10.6 to 10.10, it was called AppleScript Editor. It likely regained its original name because of the introduction of JavaScript for Automation.

See also[edit]
Applescript Editor 2.0 Download Mac Os
References[edit]
- ^'About Script Editor on Mac'. Apple Support. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^'Edit scripts with Script Editor on Mac'. Apple Support. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^'Save a script as an app in Script Editor on Mac'. Apple Support. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^'Save a compiled script in Script Editor on Mac'. Apple Support. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^'View an app's scripting dictionary in Script Editor on Mac'. Apple Support. Retrieved October 4, 2020.